Enamel Erosion: Causes and Mechanisms

What Causes Enamel Erosion?
When enamel is exposed to acids (from food, beverages or the stomach), it temporarily weakens and may lose some of its mineral content.1 Saliva will help neutralize acidity, restore the mouth's natural balance and slowly harden the enamel. However, because the tooth's recovery process is slow, if the acid attack happens frequently, the enamel does not have the chance to repair.2
Some fruit juices, wine and various fruits can be acidic and therefore potentially damaging to the teeth. Acidic foods should not and cannot easily be avoided, but care needs to be taken as to how they are consumed.3
It is not just what is consumed that causes enamel erosion, but also the way that acidic foods and drinks are held within the mouth. Holding or retaining acidic beverages in the mouth prolongs the acid exposure on the teeth, therefore increasing the risk of enamel erosion. Swishing an acidic beverage, for example, can increase the beverage's contact with the tooth or teeth, increasing the risk of tooth erosion.2
Enamel Demineralization and Remineralization Cycles
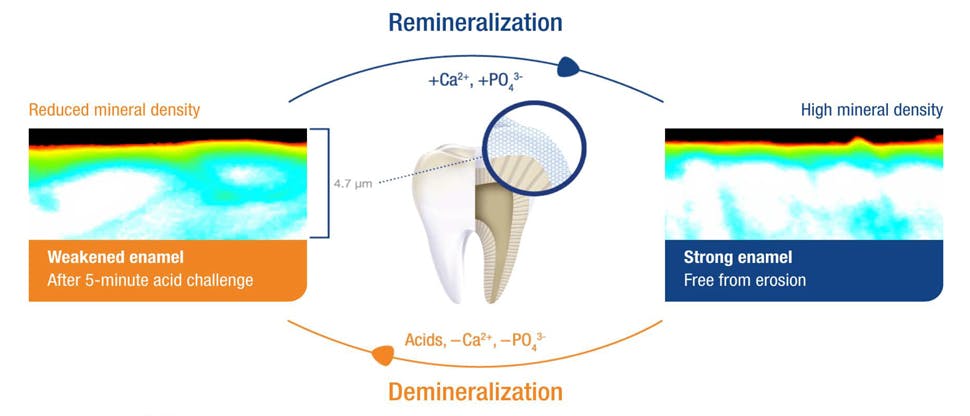
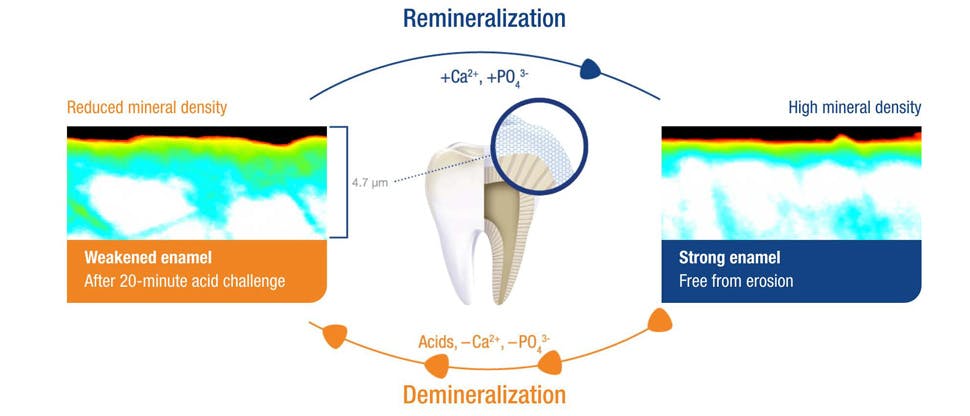
Enamel undergoes natural dynamic cycles of remineralization and demineralization, normally favoring remineralization due to mineral-rich saliva, which helps neutralize acidity and reharden enamel.2
Enamel is equipped to respond to normal daily acid exposure. Brief periods of acid exposure trigger a demineralization process that reduces the mineral density of the enamel surface, thereby weakening it.4,5
Due to mineral-rich saliva, the enamel undergoes a natural process of remineralization to restore its mineral density and the enamel is strengthened again.4,5
Frequent exposure to acids, especially over long periods, can cause the remineralization process to become overwhelmed, leaving enamel weakened. In this state, enamel is at risk of irreversible wear.4,5
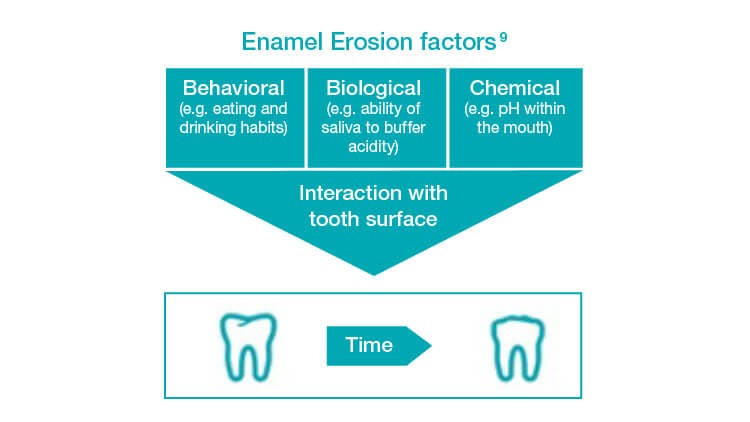
Enamel Erosion Is A Progressive Condition
There are many factors which are involved in erosive tooth wear. Biological, behavioral and chemical factors interact with the tooth surface, which over time, may either wear it away, or protect it.9
Dietary acidic exposure results in the loss of calcium and phosphorus ions from the enamel surface layer.9,10 This weakens the tooth surface, leading to an increased susceptibility to physical wear such as tooth brushing.9,10
Everyday Behaviors That Put Enamel At Risk
Up to 87% of US adults consume acidic foods and beverages everyday, putting their enamel at risk.11 Recognizing early forms of erosion may be difficult,9 so discussing specific lifestyle habits with patients at risk of developing enamel erosion can help proactively identify it.
These risk factors include:4,13
- Holding or “swishing” acidic drinks in your mouth
- Snacking frequently on acidic foodstuff
- Consuming high levels of acidic fruits and juices
Infographic adapted from Lussi et al. 20069
Patients' Enamel is at Risk From the Erosive Effects of Acidic Food and Drinks
Modern Dietary Habits Are Worsening Enamel Erosion14
Around 46% of American adolescents are already exhibiting signs of this irreversible condition.14 This is due, in part, to the way acidic foods and drinks feature prominently in modern diets.
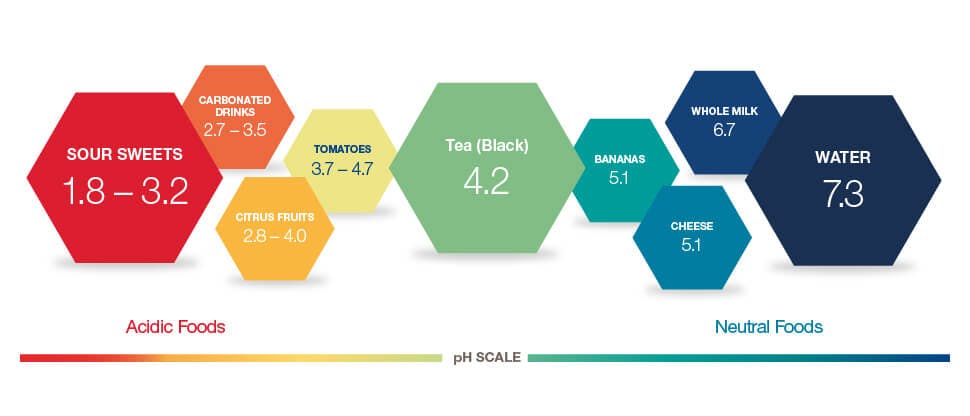
Click here to help your patients identify acids in their diets.15,16
Helping Protect Your Patients Against Enamel Erosion Caused By Dietary Acids
Impact on Patient Quality of Life
Find out about the impact enamel wear has on patients’ daily lives.